Table of Contents
Ensuring a fast and reliable Wi-Fi connection requires choosing the right Wi-Fi channel in addition to having a fast internet service and modem/routerHowever, even if you meet this requirement, your wireless internet connection can still be slow. The main reason for this is the selection of an incorrect Wi-Fi Channel.
Many users complain about slow internet speeds despite having a fast internet connection and a good modem. This is due to the widespread use of modems and the use of similar connection frequencies by other wireless devices, which can negatively affect Wi-Fi speeds. So what is a Wi-Fi channel?
What is a Wi-Fi Channel?
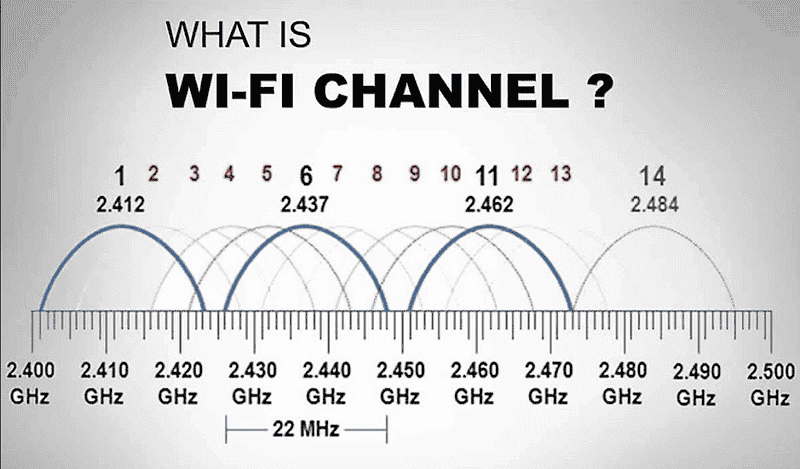
Wireless channels are frequency ranges used to transmit and receive data between your modem and wireless devices. Modern modems and routers commonly support 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz frequency represents 13 different frequency ranges, while the 5 GHz frequency represents 45 different frequency ranges (this number may vary depending on your modem and support for Wi-Fi 6).
These frequency ranges are referred to as Wi-Fi or wireless channels in our modems. The modems and routers, wireless environment units, and electromagnetic environments in our surroundings can negatively affect your wireless internet performance. For this reason, selecting the most suitable wireless channel is very important to enhance your wireless internet performance.
If your modem uses the same Wireless channel as the modems and routers in your environment, it can result in slow connections, disconnections, or even an inability to see the SSID or wireless network. This is why using different channels can always give you the best results.
What is Wireless channel bandwidth?

Wireless channels are typically divided into 20 MHz sections, which represent for example, 13 channels in the 2.4 GHz frequency. In the 2.4 GHz frequency, you can increase this bandwidth to 40 MHz, and in the 5 GHz frequency, you can go up to 80 MHz. A higher bandwidth means more data can be transmitted, making it more efficient. However, high bandwidth is more affected by environmental factors, so it might make more sense to use the 20 MHz option in 2.4 GHz networks.
Which bandwidth should be selected for 2.4 GHz?
When on the 2.4 GHz band, it’s generally recommended to use the narrower 20 MHzWireless channel width. The main reason for this is the presence of several overlapping channels in this band. As we know, overlapping Wireless channels are one of the main causes of network interference. So, if you choose a wider channel width that connects multiple overlapping channels in this band, you’re more likely to experience weaker wireless performance than expected.
Which Wireless channel bandwidth should be selected for 5 GHz?
Wider Wireless channel bandwidths, including 40 MHz and 80 MHz, are best used in the 5 GHz frequency band. This band has not only significantly more Wireless channels, but also fewer overlapping channels. Thus, it is known that the 5 GHz band is less crowded and better equipped to support wider Wi-Fi channel bandwidths, in addition to the narrow 20 MHz bandwidth.
However, selecting only 40 or 80 MHz range on 5 GHz networks may prevent your older 5 GHz-supported wireless internet devices from connecting to the network. Therefore, we recommend using your 5 GHz networks with 20/40/80 MHz options. This way, your modem or router will automatically select the channel based on the wireless internet-supported device you are using.
How to find the best Wi-Fi channel?
There are many ways to find the best wireless channel. One of the most common is Wi-Fi analysis applications for smartphones. However, since the coverage area of smartphones is not as wide as that of our modems, you can use the wireless channel analysis feature on the modem.