JTAG, an acronym for Joint Test Action Group, is a widely-used technology that plays a pivotal role in digital electronics. Initially developed for testing and debugging printed circuit boards (PCBs), It has become an essential tool for programming, debugging, and accessing embedded systems.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of JTAG, highlighting its functionality, applications, and significance in today’s technological landscape.
Understanding JTAG The Inner Workings
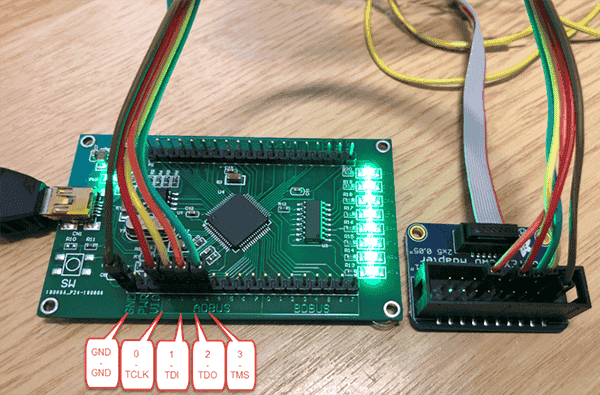
At its core, JTAG is a serial communication interface that enables communication between an external test device, typically a computer, and a device under test (DUT), ranging from a microcontroller to a complex system-on-chip (SoC). It employs a dedicated set of pins on the device, known as the JTAG interface, to facilitate data exchange. These pins include the Test Data In (TDI), Test Data Out (TDO), Test Clock (TCK), and Test Mode Select (TMS).
JTAG offers a range of functionalities that make it an indispensable tool in the electronics industry. Primarily, it allows for boundary scan testing, which enables the examination of integrated circuits (ICs) internal signals without physical access to the pins. This non-intrusive testing technique ensures excellent fault coverage and quicker identification of faults during production testing.
Furthermore, enables in-system programming, where the device can be programmed while still mounted on the PCB, eliminating the need for individual programming interfaces for each component. This feature simplifies manufacturing, reduces costs, and facilitates firmware updates in field-deployed devices.
JTAG and Debugging – Unleashing the Power
JTAG’s debugging capabilities are highly regarded by hardware and software developers alike. By utilizing JTAG, engineers can halt the operation of a processor, access its internal registers, examine memory contents, and step through the code instruction by instruction. This level of visibility and control proves invaluable in identifying and rectifying bugs, optimizing performance, and enhancing overall system reliability.
JTAG finds applications across various industries, ranging from aerospace and automotive to consumer electronics. In the aerospace sector, JTAG plays a vital role in verifying avionics systems’ integrity, ensuring critical flight systems’ safety and reliability. In the automotive industry, it aids in diagnosing and debugging complex electronic systems, such as engine control units (ECUs) and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Consumer electronics also benefit significantly from JTAG. Mobile phones, tablets, gaming consoles, and other electronic devices leverage JTAG for testing, programming, and debugging during manufacturing and maintenance phases. It allows efficient and cost-effective testing of complex digital circuits integrated into these devices.
JTAG Devices for Mobile Phones
JTAG devices that support mobile phones are essential tools for testing, programming, and debugging processes in mobile device development. Here are some JTAG devices that are compatible with various popular mobile phone brands:
RIFF Box: RIFF Box is a powerful JTAG device that supports operations for multiple mobile phone brands such as Samsung, HTC, LG, and Nokia. It offers comprehensive functionality for JTAG operations on these devices.

Z3X Easy JTAG: Z3X Easy JTAG is a popular choice for Samsung mobile phones. It supports JTAG and eMMC operations, enabling software repairs, data recovery, and debugging processes.
Medusa Pro Box: Medusa Pro Box is another versatile JTAG device that supports mobile phone brands, offering advanced features for JTAG operations. It allows efficient testing, programming, and debugging on various mobile phone models.
Octoplus Pro Box: Octoplus Pro Box is a comprehensive JTAG device that supports multiple mobile phone brands, including Samsung, LG, Sony, and others. It enables various operations, such as firmware updates, unlocking, and repair tasks.

These devices provide mobile phone technicians and developers with the tools to perform advanced testing, programming, and debugging operations. By leveraging the capabilities of these devices, professionals can enhance their efficiency, speed up the development process, and ensure the optimal performance of mobile devices.