Table of Contents
The power supply unit (PSU) is often one of the least considered components in a computer. Most basic users don’t research or give power supplies much importance when building a PC. While the PSU might not directly affect gaming performance, it plays a crucial role in distributing power to PC components, making it a vital piece of hardware.
With hundreds of power supplies available in the market, the multitude of brands and models can make the decision-making process challenging. Making the wrong PSU choice can lead to immediate or gradual adverse effects that impact your system’s performance.
The power supply is often considered a gaming machine’s or any computer’s heart. Just as the heart supplies blood to all organs, the PSU’s task is to ensure clean and continuous electrical flow to your PC components. When power distribution is not provided accurately and healthily, unexpected malfunctions can occur, the system might shut down, and multiple components within the system might become unusable.
Indeed, attention should be given to the power supply. This article will discuss factors to consider when purchasing a PSU.
What is a Power Supply Unit (PSU)?
The Power Supply Unit (PSU) converts the AC current from your wall outlet into the DC current required by PC components to operate. Unlike household appliances, PC components require a constant and stable flow of DC current for proper operation. The PSU facilitates the efficient and clean current conversion from AC to DC and then delivers it to specific components as needed.
While PSUs might not directly contribute to a computer’s aesthetics or performance, you’ll notice their importance when any issues arise, and the lights won’t turn on. Hence, the power supply is a fundamental and crucial PC component that requires attention. What to Consider When Buying a PSU?
There are several vital features when purchasing a power supply unit. The list and terms might seem dull as you go through them, but when taken individually, they’re simple enough, and we’ll strive to keep explanations simple.
Capacity
Before selecting a PSU, you must determine how much power you need to run your computer. It’s important to note that the PSU doesn’t “provide” power, but rather, components “draw” the required power. Buying a larger PSU won’t increase your electricity bill proportionally.
There are two ways a user can estimate the power their system needs. For instance, our reviews detail the instantaneous power drawn by critical hardware like the CPU and GPU. By referring to our reviews and tests, you can calculate the power needed by specific components and gain a rough estimate.
How to Measure Computer Power Consumption?
Two components in a computer consume high power: the graphics card (GPU) and the central processing unit (CPU). While every component requires some power, these two account for significant portions. RAM and motherboard manufacturers often don’t list power consumption values as they are generally low-power consumers (similar to storage drives). To gain a general understanding, you can refer to the following table:
Component Hardware Type General Power Range (watts, W)
CPU High-end desktop (10+ cores) 30 (idle) | 120-250 (peak)
Mid-range desktop (6-8 cores) 15 (idle) | 60-150 (peak)
Low-end desktop (4-6 cores) 15 (idle) | 60-120 (peak)
GPU High-end graphics card 30 (idle) | 250-400 (peak)
Mid-range graphics card 20 (idle) | 175-220 (peak)
Low-end graphics card 20 (idle) | 75-150 (peak)
Motherboard ATX 4 (idle) | 15-30 (peak)
Micro-ATX | Mini-ITX 2 (idle) | 5-20 (peak)
DRAM 8 GB DDR4/5 1 (idle) | 5 (peak)
SSD M.2 NVMe SSD 0.5 (idle) | 6 (peak)
HDD SATA 3.5″ 7200 RPM hard drive 3 (idle) | 8 (peak)
Cooling Case/cooler fan 2-5 (peak)
The table provides an overview of the power consumption levels of different components, allowing you to make approximate calculations. As an additional detail, installing the same CPU on different motherboard models might result in different power values. Premium models that allow overclocking generally have higher maximum power values.
Another option is to use power supply calculation tools like OuterVision, Cooler Master, and BeQuiet!. These calculators provide estimated suggestions based on your components. However, it’s important to note that these tools often overestimate component power draw and recommend PSUs with higher capacity than necessary.
These tools rely on default power values provided by component manufacturers, leading to variable results. For example, for the same system, Cooler Master might recommend a 561W PSU, while BeQuiet! Suggest a 692W maximum power estimate. This shows a considerable difference. As mentioned, such calculation tools might not provide accurate results, but they can offer clues about the needed PSU.
If you want to delve into details, you can check the technical specifications of components on their official product pages. Significant companies like AMD, Intel, and NVIDIA often provide detailed information. However, finding all the details might take work.
In general, leaving a margin of around 150-200 watts in your power supply capacity is advisable. This margin can be lower for entry-level systems; for a system drawing 350W, a 450W PSU would suffice. For example, if all your components draw around 650W under load, opting for a high-quality 800-850W PSU would be a good choice. Additionally, this can save you from trouble when upgrading your system or provide room for overclocking in the future.
Extra headroom is a good idea, but you should stay moderate. Getting a 1000W PSU for a computer consuming 600-650W under load would be impractical. You would end up paying for unused capacity.
Efficiency: 80 Plus Certifications
Another significant factor to consider when purchasing is the PSU’s efficiency. Power supplies come with various efficiency levels and different “rating” labels. As previously mentioned, the PSU converts AC power from the wall into the DC power required by components, and some energy is lost in this process as waste heat.
A good power supply converts around 80% of the incoming power into DC power. A high-quality product can convert more than 90% of the incoming power. In essence, higher efficiency in a power supply is better. We have an extensive article on this topic:
What is the 80 Plus Certification?
The 80 Plus (80+) name has been in use since 2004, initiated as a voluntary certification program to encourage the industry to design more efficient PSUs. To obtain the certification, a PSU needs to achieve efficiency of over 80% at 20%, 50%, and 100% loads. Additionally, it needs to have a power factor of 0.9 or higher at 100% load.
The 80 Plus certification has several levels, each indicating a different efficiency level.
80 Plus: Achieving 80% efficiency at 20%, 50%, and 100% loads.
80 Plus Bronze: Achieving 82% efficiency at 20% load, 85% efficiency at 50% load, and 82% efficiency at 100% load.
80 Plus Silver: Achieving 85% efficiency at 20% load, 88% efficiency at 50% load, and 85% efficiency at 100% load.
80 Plus Gold: Achieving 87% efficiency at 20% load, 90% efficiency at 50% load, and 87% efficiency at 100% load.
80 Plus Platinum: Achieving 90% efficiency at 20% load, 92% efficiency at 50% load, and 89% efficiency at 100% load.
80 Plus Titanium: Achieving 90% efficiency at 10% load, 92% efficiency at 20% load, 94% efficiency at 50% load, and 91% efficiency at 100% load.Why is the 80 Plus Certification Important?
Choosing a power supply with a higher 80 Plus certification means it will waste less energy as heat, and your electricity bill will be lower. Higher efficiency also often correlates with better overall PSU quality, as achieving higher efficiency requires better components and design.
Remember that higher certification levels usually come with higher price tags. However, the initial cost difference can be balanced out by the long-term energy savings and potential hardware protection.
A PSU with a higher 80 Plus certification is generally recommended if your budget allows. For gaming systems or PCs that run for extended periods, a Gold or Platinum-rated PSU might be a good choice. A Bronze or Silver-rated PSU might suffice for budget-oriented systems that aren’t under heavy load often.
Form Factor: ATX, SFX, and More
Power supplies come in different form factors; the most common one is the ATX form factor. The ATX form factor PSU is the standard size and shape used in most desktop PCs. However, there are smaller and larger form factors available for different applications.
For instance, the SFX (Small Form Factor) power supplies are designed for compact or mini-ITX cases. These are smaller in size compared to standard ATX power supplies. They allow for more space within the case, essential in compact builds where every inch counts.
There are also more prominent form factors, like the Extended ATX (E-ATX) or the Flex ATX, designed for high-performance systems or specialized cases. Before purchasing a PSU, ensure it matches your case’s form factor. Most cases specify which form factors of power supplies they can accommodate.
Power Supply Components
Consumers often need to be better informed about the components inside a product, which is quite normal. However, the components of a PSU (Power Supply Unit) are crucial. Cheaper and lesser-known products tend to use cheaper electronic components, which can affect both the power output of the system and the overall longevity of the power supply. You can refer to reviews to determine whether a PSU utilizes quality components.
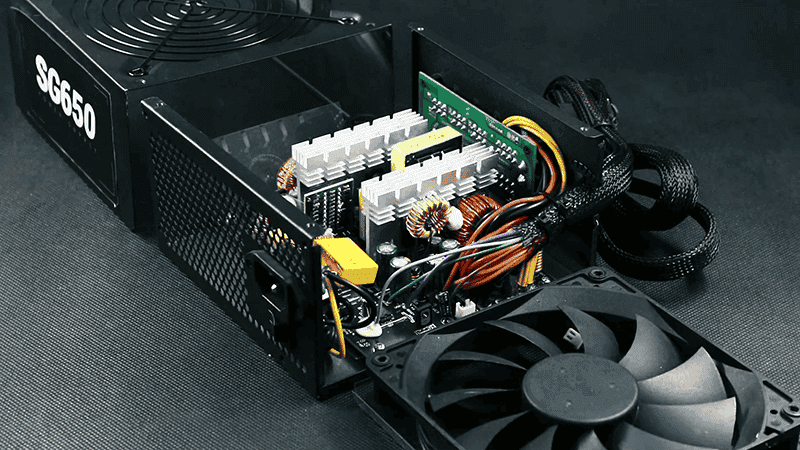
On the other hand, you can also gather information about products by visiting their official websites. You might come across terms like “Japanese Capacitors” or “Premium Chokes.” In the world of PSUs, Japanese capacitors have gained quite a reputation. Power supplies with these components are generally pricier but of higher quality.
Another effective method to assess the quality of components within a PSU is to compare their weights. This might sound amusing, but heavier PSUs are usually of higher quality than lighter ones. In other words, they are often manufactured using better components. It’s important to note that these insights are based on general assumptions, so conducting thorough research and consulting professional reviews for accurate information is advisable.
Connectors and Cable Management
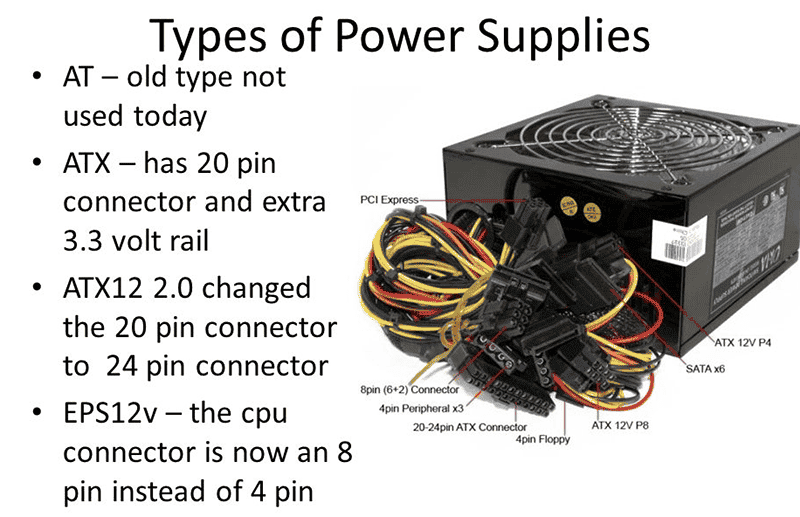
Having suitable connectors is crucial to ensure compatibility with your components. Modern power supplies come with various cables and connectors for motherboards, graphics cards, storage devices, and fans. Before purchasing a PSU, ensure it has the necessary connectors to power all your components.
Additionally, cable management is an important consideration. Modular and semi-modular power supplies allow you to connect only the cables you need, reducing cable clutter and improving airflow within the case. This not only enhances aesthetics but also makes the building process more manageable.
On the other hand, non-modular power supplies come with a fixed set of cables, which might result in unused cables filling up the case. This can impede airflow and make the interior look messy.
When selecting a power supply, consider your cable management preferences and the specific requirements of your case and components.
Brand and Warranty
Choosing a reputable brand for your power supply is essential. Established brands often have a history of producing reliable and high-quality PSUs. Brands like Corsair, EVGA, Seasonic, Cooler Master, and Be Quiet! are known for their quality power supplies.
A more extended warranty period usually indicates a more reliable power supply. A standard warranty period for power supplies is around 3 to 5 years, but some manufacturers offer up to 10 years for their high-end models. A more extended warranty provides peace of mind and reflects the manufacturer’s confidence in their product’s durability.
Final Remarks
The power supply unit (PSU) is a crucial component of your computer that often doesn’t receive the attention it deserves. It’s responsible for providing clean and stable power to all your PC components, making it vital for your system’s overall health and performance. When choosing a PSU, factors like capacity, efficiency, form factor, connectors, and brand reputation should be considered.
By calculating the power consumption of your components, selecting an efficient PSU with an appropriate 80 Plus certification, ensuring compatibility with your case’s form factor, and choosing a reliable brand, you can make an informed decision and ensure a stable and efficient power supply for your computer. While it might not be the most exciting part of building a PC, selecting the proper PSU can significantly impact your system’s longevity and performance.


