Table of Contents
In the world of display technology, comprehending the differences between various screen panels is crucial for making informed decisions. Whether you’re a gamer, a graphic designer, or just a regular user, the type of screen panel you choose can significantly impact your experience. This article delves into the most common types of screen panels: IPS, TN, VA, OLED, AMOLED, QLED, LCD, and LED. Our target keyword for this comprehensive guide is “different types of screen panels.”
What is IPS?
In-plane switching (IPS) panels are LCD technology known for their superior color reproduction and wide viewing angles. Developed to overcome the limitations of TN panels, IPS technology is widely used in high-end monitors, smartphones, and tablets.
Features of IPS Panels
- Color Accuracy: IPS panels excel in color accuracy, a crucial feature for graphic design and photo editing. This feature ensures your work is displayed as intended. Viewing Angles: With viewing angles up to 178 degrees, IPS panels maintain color consistency from different perspectives.
- Response Time: IPS panels typically have slower response times than TN panels, but advancements have improved this aspect.
IPS Panel Table
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Color Accuracy | High, suitable for professional color work |
| Viewing Angles | Up to 178 degrees |
| Response Time | Moderate, newer models have improved times |
| Contrast Ratio | Good, but generally lower than VA panels |
| Applications | Professional monitors, tablets, smartphones |
TN (Twisted Nematic) Screen Panels
What is TN?
Twisted Nematic (TN) panels are one of the oldest types of LCD technology. They are known for their fast response times and affordability, making them popular among gamers and budget-conscious consumers.
Features of TN Panels
- Response Time: TN panels have the fastest response times, often below 1 ms, making them ideal for fast-paced gaming.
- Color Reproduction: TN panels generally have poorer color accuracy and viewing angles than IPS and VA panels.
- Cost: These panels are typically more affordable, making them a cost-effective option.
TN Panel Table
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Color Accuracy | Moderate to low, not suitable for professional color work |
| Viewing Angles | Narrow, colors can shift when viewed from angles |
| Response Time | Very fast, often below 1ms |
| Contrast Ratio | Lower than IPS and VA panels |
| Applications | Gaming monitors, budget monitors |
VA (Vertical Alignment) Screen Panels
What is VA?
Vertical Alignment (VA) panels are a type of LCD technology that offers a balance between TN and IPS panels. They provide better color reproduction and viewing angles than TN panels and higher contrast ratios than IPS panels.
Features of VA Panels
- Contrast Ratio: VA panels have the highest contrast ratios among LCD types, providing deeper blacks and more vivid colors.
- Viewing Angles: Better than TN panels but slightly less than IPS panels.
- Response Time: Slower than TN panels but adequate for most uses.
VA Panel Table
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Color Accuracy | Good, better than TN, but less than IPS |
| Viewing Angles | Moderate, better than TN but less than IPS |
| Response Time | Moderate, slower than TN but adequate |
| Contrast Ratio | Very high, best among LCD types |
| Applications | General-purpose monitors, TVs |
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) Screen Panels
What is OLED?
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) technology uses organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. Unlike LCD panels, OLEDs do not require a backlight, allowing for thinner designs and better power efficiency.
Features of OLED Screen Panels
- Color Accuracy: OLED panels provide exceptional color accuracy and contrast ratios, producing true blacks.
- Viewing Angles: Excellent, with no significant color shifts.
- Response Time: Very fast, making them ideal for gaming and multimedia applications.
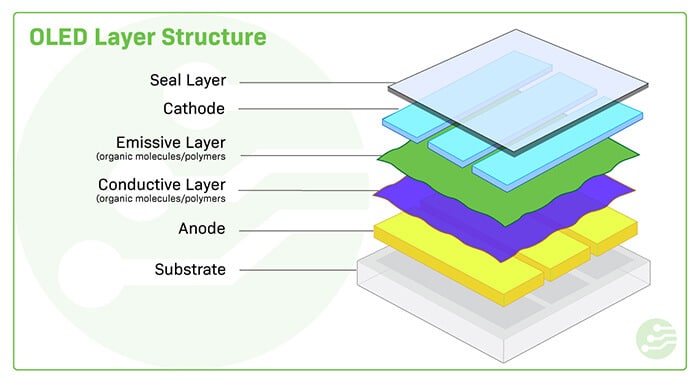
OLED Panel Table
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Color Accuracy | Excellent, with true blacks and vibrant colors |
| Viewing Angles | Excellent, no significant color shifts |
| Response Time | Very fast, ideal for gaming |
| Contrast Ratio | Infinite, true blacks |
| Applications | High-end TVs, smartphones, professional monitors |
AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode)
What is AMOLED?
Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) is a type of OLED that uses an active matrix to control the pixels. This technology is commonly used in smartphones and high-end displays.
Features of AMOLED Panels
- Color Accuracy: Like OLED, with excellent color reproduction and deep blacks.
- Viewing Angles: Excellent, with consistent colors from all angles.
- Response Time: Very fast, making it suitable for multimedia applications.
AMOLED Panel Table
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Color Accuracy | Excellent, similar to OLED |
| Viewing Angles | Excellent, with no significant color shifts |
| Response Time | Very fast, ideal for multimedia applications |
| Contrast Ratio | Infinite, true blacks |
| Applications | Smartphones, high-end TVs, tablets |
QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) Screen Panels
What is QLED?
Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode (QLED) technology uses quantum dots to enhance LED-backlit LCD panels’ brightness and color accuracy. Samsung developed this technology and uses it in its high-end televisions.
Features of QLED Panels
- Color Accuracy: QLED panels offer vibrant colors and high brightness levels.
- Viewing Angles: Improved over traditional LED panels, but less good than OLED.
- Response Time: Fast, suitable for most applications.
QLED Panel Table
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Color Accuracy | Very good, vibrant colors and high brightness |
| Viewing Angles | Good, but not as good as OLED |
| Response Time | Fast, suitable for most uses |
| Contrast Ratio | High, but not as high as OLED |
| Applications | High-end TVs, gaming monitors |
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
What is LCD?
From its humble beginnings, Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) technology has evolved to become one of the most common display technologies used in monitors, televisions, and other devices.
Features of LCD Panels
- Color Accuracy: Varies widely depending on the type of LCD panel (e.g., IPS, TN, VA).
- Viewing Angles: Varies, with IPS offering the best angles.
- Response Time: Varies, with TN panels offering the fastest response times.
LCD Panel Table
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Color Accuracy | Varies, with IPS being the best |
| Viewing Angles | Varies, with IPS being the best |
| Response Time | Varies, with TN being the fastest |
| Contrast Ratio | Varies, with VA being the highest |
| Applications | Monitors, TVs, laptops |
LED (Light Emitting Diode)
What is LED?
Light Emitting Diode (LED) panels are essentially LCD panels that use LED backlighting instead of traditional CCFL backlighting. This allows for thinner designs and better energy efficiency.
Features of LED Panels
- Color Accuracy: Improved over CCFL-backlit LCDs, with better brightness and contrast.
- Viewing Angles: Similar to the underlying LCD technology (e.g., IPS, TN, VA).
- Response Time: Similar to the underlying LCD technology.
LED Panel Table
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Color Accuracy | Improved over CCFL-backlit LCDs |
| Viewing Angles | Similar to the underlying LCD technology |
| Response Time | Similar to the underlying LCD technology |
| Contrast Ratio | Improved over CCFL-backlit LCDs |
| Applications | Monitors, TVs, laptops |
Which Display Panel is Used for What Purpose
IPS (In-Plane Switching)
IPS panels are ideal for professional work where color accuracy and wide viewing angles are crucial, such as graphic design, photo editing, and video production.
TN (Twisted Nematic)
TN panels are best suited for gaming and applications requiring speedy response due to their low input lag and high refresh rates.
VA (Vertical Alignment)
VA panels are great for general-purpose use and watching movies, thanks to their high contrast ratios and sound color reproduction.
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode)
OLED panels are perfect for high-end televisions and smartphones that require true blacks, high contrast ratios, and vibrant colors.
AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode)
AMOLED panels are used in high-end smartphones and televisions, offering excellent color accuracy, deep blacks, and fast response times.
QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode)
QLED panels are used in high-end televisions, providing bright images with vibrant colors and good contrast.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
LCD panels are standard in monitors, laptops, and budget televisions, balancing performance and cost.
LED (Light Emitting Diode)
LED panels, essentially LED-backlit LCDs, are used in various devices, including monitors, TVs, and laptops, for improved brightness and energy efficiency over traditional CCFL-backlit displays.
Screen Panel Manufacturers
IPS (In-Plane Switching)
- LG Display
- AU Optronics
- Sharp
- Japan Display Inc. (JDI)
- BOE Technology Group
TN (Twisted Nematic)
- Samsung
- LG Display
- AU Optronics
- Innolux Corporation
- Chi Mei Corporation
VA (Vertical Alignment)
- Samsung
- AU Optronics
- Innolux Corporation
- BOE Technology Group
- Sharp
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode)
- Samsung Display
- LG Display
- Sony
- BOE Technology Group
- Visionox
AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode)
- Samsung Display
- LG Display
- BOE Technology Group
- Visionox
- Tianma Microelectronics
QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode)
- Samsung
- TCL
- Hisense
- Vizio
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
- LG Display
- Samsung
- AU Optronics
- BOE Technology Group
- Innolux Corporation
LED (Light Emitting Diode)
- Samsung
- LG Display
- AU Optronics
- BOE Technology Group
- Sharp
Comprehending the different types of screen panels is essential for choosing the correct display for your needs. Each panel type has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on your specific requirements, whether for gaming, professional work, or general use. By considering factors like color accuracy, viewing angles, response time, and contrast ratio, you can make an informed decision and enjoy a better visual experience.



